Professor Zhuge Qichuan published a paper in Clinical Infectious Diseases to share Wenzhou’s Anti-COVID-19 measures
 2020-04-14
2020-04-14
 Cooperation & Communication Dept.
Cooperation & Communication Dept.
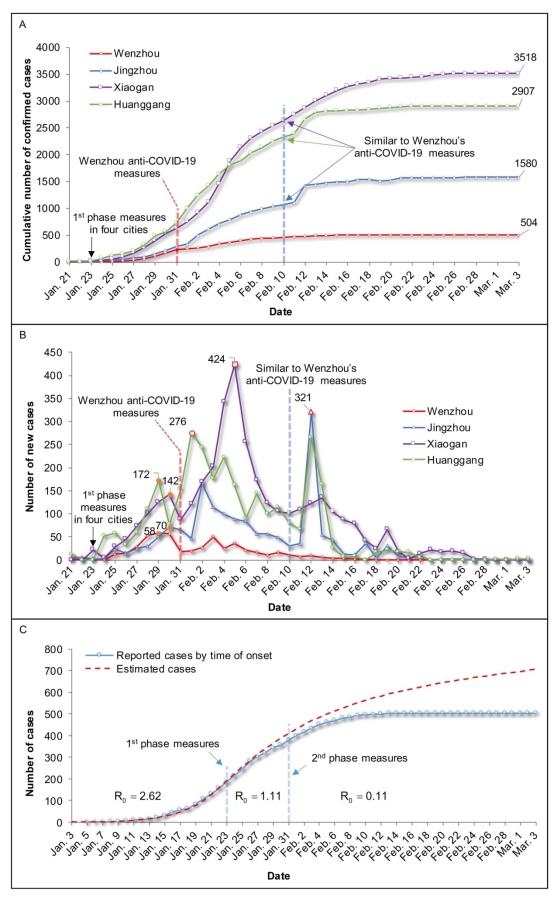
Having reviewed Wenzhou’s anti-COVID-19 measures since Jan 17, and conducted a data comparison with several cities in Hubei through data model, the research team led by Professor Zhuge Qichuan of the Neurosurgery Department of our hospital summarized the effects of Wenzhou’s anti-epidemic measures on epidemic control and prevention as well as disease treatment and wrote an academic paper entitled New measures for COVID-19 response: a lesson from the Wenzhou experience, which has been published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, an international authoritative epidemiology journal. (Top in area 1 of Chinese Academy of Sciences, impact factor 9.055).
This paper systematically analyzed and summarized Wenzhou’s epidemic prevention and control measures at two phases, namely, Phase 1 prevention and control measures and Phase 2 prevention and control measures. Phase 1 prevention and control measures from January 17 to January 30 mainly include (1) collective treatment for confirmed and suspected patients; (2) screening all returnees from Wuhan through big data, and persuading them to be quarantined at home for 14 days; (3) collective quarantine for close contacts of confirmed cases. Phase 2 prevention and control measures from January 31 to February 20 (Wenzhou Anti-COVID-19 Measures) aim to accurately find the source of infection, completely cut off the transmission route and implement collective treatment, mainly including (1 )city lockdown, namely, all traffic in and out of Wenzhou such as the airports, wharves, high-speed railway stations and bus stations except five entrances on expressways for the purpose of transporting prevention and control materials and necessities of life with strict inspection; (2)district lockdown, namely, all collective activities must be cancelled including shopping malls, public entertainment facilities, group meetings, restaurants and hotels, in addition, all residents must be quarantined at home and managed in the form of grids with management and villages as the unit, a post set up to check, inquire, register the body temperature of all people and the daily necessities distributed at fixed points in real time; (3) screening, namely, big data, the Internet, resident investigation and hotel investigation were used to find out high-risk residents in time so that all the close contacts and suspected cases can be collectively quarantined and all the infected cases can be diagnosed timely and collectively treated; (4) collective treatment: a medical expert group was set up to deal with epidemiological investigation and treatment of confirmed patients. Critically ill patients received collective treatment in the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, and those with mild symptoms and suspected patients received collective treatment in medical centers of various counties and urban areas, at the same time, all close contacts received collective medical quarantine. In addition, nucleic acid testing was conducted as fast as possible in a bid to realize early diagnosis, early quarantine, early treatment and collective treatment.
This paper summarized the effects of Wenzhou’s anti-COVID-19 measures on the epidemic control. After Wenzhou implemented the Phase 1 measures, it can be found that the imported cases decreased significantly, indicating that these measures are effective in preventing imported cases. After Phase 2 measures were implemented, new cases dropped immediately and there was no reported new cases in 17 days. From the first confirmed case on Jan 17 to the last case on Feb 17, Wenzhou only spent 31 days in completely controlling the epidemic. Calculated and measured through data model, the R0 value of Wenzhou epidemic in the outbreak period was 2.62 but that after the implementation of Wenzhou’s prevention and control measures gradually fell to 0.11. In this paper, the epidemic control and prevention in Wenzhou and three cities of Wuhan (Huanggang, Xiaogan, and Jingzhou) was compared. Cities around Wuhan, Huanggang, Xiaogan, and Jingzhou, are similar to Wenzhou in terms of time of onset, population, as well as the prevention and control measures before January 31, and even in terms of the spread of epidemic. After Wenzhou implemented strict Phase 2 prevention and control measures on Jan 31, the onset curves of the four cities showed significant difference.
This paper summarized the effect of anti-COVID-19 measures on the treatment of diseases. Among the 504 cases in this group, 8 cases were critically ill and 62 cases were severely ill, accounting for 13.9%, 1 death, accounting for 0.2%. The death rate in Wenzhou is lower than that in Wuhan and the whole country, and no medical staff was infected in Wenzhou.
COVID-19 is characterized by high infectivity and rapid spread speed, therefore, Wenzhou’s prevention and control measures are effective in quickly controlling the epidemic. Early detection, early quarantine, early diagnosis, early treatment and collective treatment are very important for the prognosis of the disease. As critically ill patients should receive collective treatment as soon as possible with multidisciplinary collaboration and comprehensive diagnosis and treatment implemented by respiratory medicine department, infectious diseases department, otolaryngology department, anesthesiology department, and cardiology department on the basis of Department of Critical Care Medicine. At the same time, it is expected that Wenzhou’s anti-COVID-19 measures can be of some reference value for other cities with severe epidemic situation throughout the world.
(Link to https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa386 PMID: 32246149)


